A recent article in the RBA Bulletin, Climate Change and Financial Risk, highlighted that climate scenario analyses by financial regulators (both in Australia and abroad) have not to date found that climate change presents a systemic risk to national financial systems. However, these exercises feature some crucial weaknesses. For example, they have neglected physical risk to businesses outside agriculture, relied on climate models that do not capture the full extremes of potential future climate impacts, and assumed, despite mounting evidence to the contrary, that insurance is always available (even if more expensive) to business. They have also, as noted in a post-mortem on the Bank of England’s Climate Biennial Exploratory Scenario (CBES), excluded: ‘tipping points, feedback loops, supply chain disruption, indirect impacts, geopolitical risks, migration and conflict’.
It is clearly far too soon to rule out systemic climate risk. But even if the financial system can withstand these stressors, banks can (and some surely will) lose money, and there are clear opportunities to manage their climate risk more effectively. A key question for banks is, how can climate risk be effectively integrated into credit risk processes?
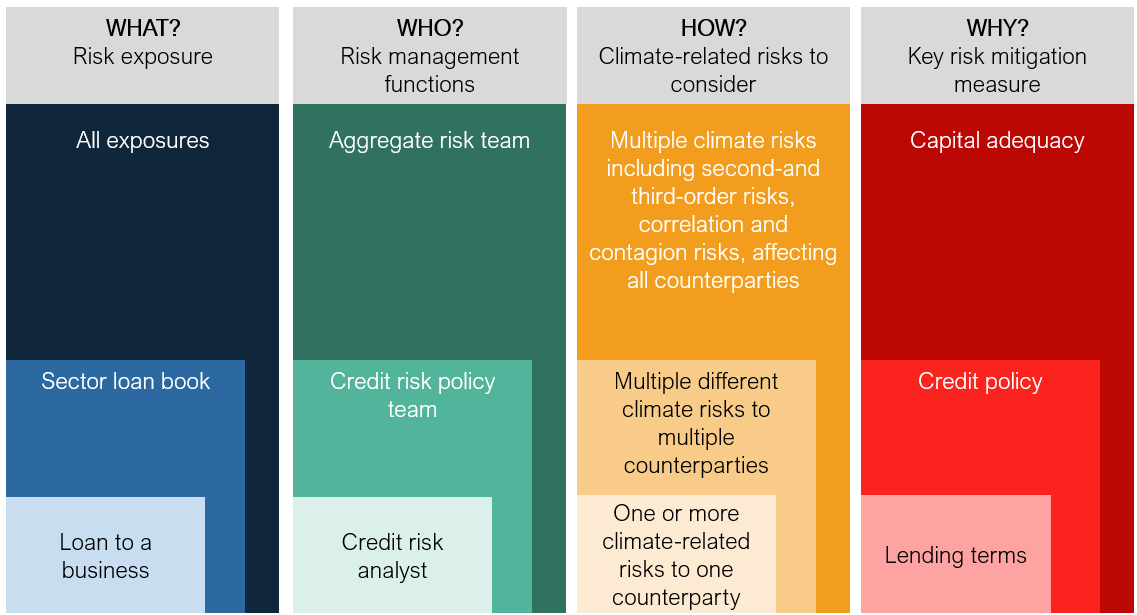
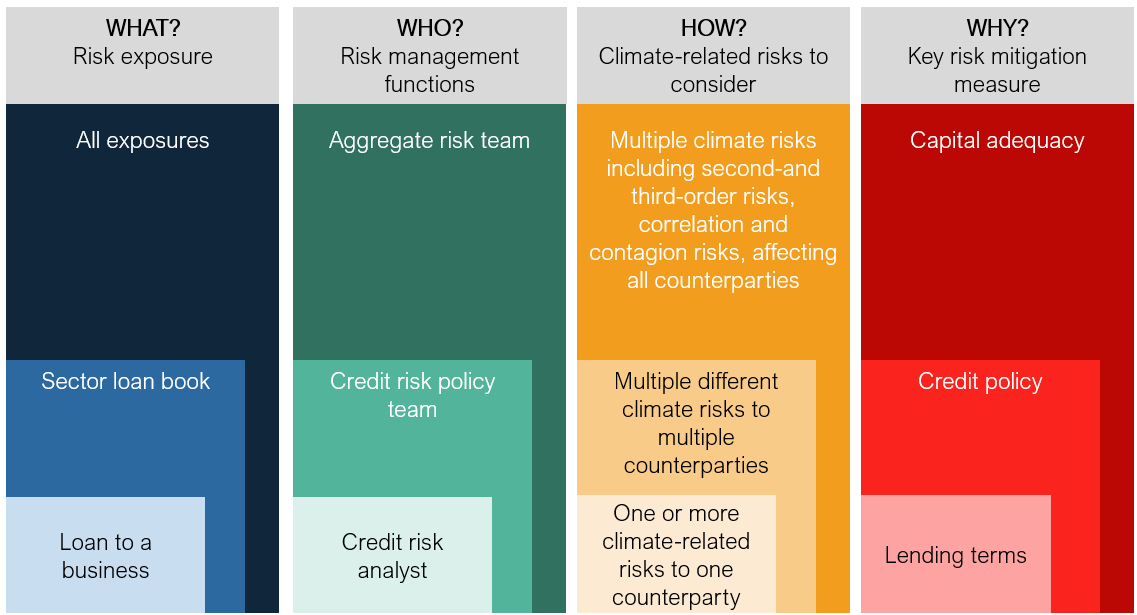
In particular, the challenge is moving from these broad-based processes run by regulators, looking at the capital adequacy of the book, through to decision-useful insights to shape front-line decisions as described in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Applying insights for front line decisions
The way forward requires:
- Smarter scenario analysis to understand the chains of causality between climate change and credit losses, and where to focus future effort
- Targeted enhancement of climate risk modelling for sectors, locations and client types with higher inherent risk
- Building institutional capability to make the right decisions at the right point in the transaction lifecycle, to ensure credit decisions take climate into account.
In this article we step through these three critical aspects of understanding climate risk.
Smarter scenario analysis
The first generation of climate-related financial risk scenarios focused on fairly narrowly defined climate risks – whether physical (e.g. decreased rainfall leads to lower wheat production), or transition (e.g. closure of coal-fired generators leads to localised impacts on employment and housing values). This was the approach taken by APRA’s Climate Vulnerability Assessment (CVA)[1].
In Energetics’ work, we find that more significant impacts frequently lie beyond the immediate activities of the firms we’re working with – whether in their supply chain or their customer base.
Additionally, acute stresses (such as bushfires), coincident or compound events (e.g. impacts on regional mortgage markets where agriculture faces physical risks) and socio-economic responses (e.g. policy changes), tend to be under-represented in risk modelling, but represent material risks, particularly if adaptation is either not possible (impacting collateral value) or prohibitively expensive (impacting serviceability).
Finally, transition and physical risks tend to be considered separately, but they will affect us at the same time, and they interact. We cannot afford to keep treating them as discrete.
Australia’s big banks have already developed significant capability through the climate risk work they have done to date, independently and through the CVA. But they have only scratched the surface. More sophisticated scenario analysis is needed to explore chains of climate risk within their lending books, and identify priorities for risk mitigation (see Chapter 7 of this report, which we developed in collaboration with CSIRO and KPMG, for more detail).
Modelling drivers of credit risk
Once priority areas have been identified, banks can work to develop a more sophisticated understanding and quantify the potential risks.
Energetics has worked with a number of different banks on pioneering the analysis of climate risk to agribusiness. The approach we developed can be broadly applied to any other sector. Other approaches we use – for example, event-driven scenarios or war-games – can be used to gain particular insight into acute risks and stakeholder responses. These techniques can be particularly effective in understanding sequential or multi-hazard risks.
Building institutional capability to manage risk
Identifying that industries or locations are at risk under a particular climate scenario won’t necessarily identify those facing a credit loss. Not all customers are the same, and customers can take actions to manage their risk. Banks can gain an advantage by proactively responding to the insights they’re gaining.
Banks may be tempted to respond by adding an overlay on credit risk scores for clients who match the pattern identified in the scenario analysis. While this may be quick to implement, it misses important nuance as it treats clients equally, and misses the opportunity to support clients in mitigating the risks.
But before banks can move to a more sophisticated approach they will almost certainly need to address data gaps around how climate risk will impact their clients. This may be as simple as having accurate location data for the collateral backing the loans (which is frequently different to the contact details of the borrower). Or it can require more detailed enquiries, such as understanding critical elements of a company’s supply chain, or certain features of the physical property.
While there are some top-down sources for geospatial and climate risk data, or richer sources about client assets (for example CoreLogic’s partnership with CSIRO’s RapidRate), much of the data will need to come from customers. The cost and customer impact of sourcing this additional data highlights the need to prioritise, based on insights from the scenario analysis and modelling steps.
Once banks have this richer data, they can take a more targeted approach to risk management by incorporating climate risk into individual credit scoring. This can highlight customers with an increased probability of default due to variability in revenue or costs. It can also highlight where current asset valuations may not adequately reflect future climate risks, and therefore where a lower LVR may be appropriate.
Finally, by equipping staff with relevant insights and appropriate training, banks can be proactive in supporting their clients with identifying and investing in new climate risk responses. This has the dual benefit of de-risking lending, and potentially creating new revenue streams in financing customer’s adaptation to and mitigation of climate risks.
Stress tests set by regulators have defined a minimum standard, and banks have passed so far. But the rewards could be great for banks who can treat climate risk as much more than a compliance activity, and instead build the capability to proactively manage risks and support their clients.
Related insights
-
Policy and legislation Prepare for successively tougher climate-related financial disclosuresREAD MORE -
Climate resilience Nowhere to hide - Corporate climate action in the age of hostile analyticsREAD MORE -
Climate risk and resilience Dr Nick Wood: work cited in US Economic Report of the PresidentREAD MORE